Java CompletableFuture 사용법
Java로 복잡한 스레드 처리를 할 수 있는 CompletableFuture 사용법에 대해서 알아본다.
CompletableFuture
Java8에서는 CompletableFuture가 도입되어 보다 복잡한 Thread 처리를 할 수 있게 되었다.
CompletableFuture를 사용하면 결과를 얻은 후 결과를 처리 할 수 있다. 또한, 여러 CompletableFuture의 완료를 기다리고 처리를 수행하거나, CompletableFuture 중 하나가 완료될 때까지 기다리면서 처리할 수 있다.
처리의 결과로 어떤 값을 돌려주고, 그것을 사용해 다른 처리를 한다.
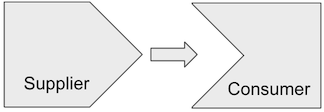
어떤 값을 돌려주는 것은 Supplier이고, 값을 받고 처리를 하는 것은 Consumer을 조합해 보도록 하겠다.
package com.devkuma.basic.completablefuture;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class SupplyAndConsume {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Supplier<Integer> initValueSupplier = () -> 100;
Consumer<Integer> valueConsumer = value -> System.out.println(value);
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(initValueSupplier)
.thenAcceptAsync(valueConsumer);
future.get(); // 결과 가져오기
}
}
실행 결과:
100
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(Supplier)- 비동기적으로
Supplier를 처리하면서,CompletableFuture의 인스턴스를 돌려준다.
- 비동기적으로
CompletableFuture.thenAcceptAsync(Consumer)CompletableFuture인스턴스의 처리가 종료하면 반환값을 건네주어 Consumer의 처리를 실행한다.
처리의 결과로 어떤 값을 돌려주고, 그것을 변환하여 반환하고, 그 반환 값을 처리를 한다.
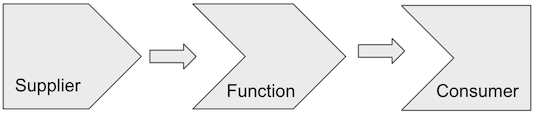
어떤 값을 돌려주는 것은 Supplier이고, 변환은 Function으로, 그 반환 값을 받아 처리를 하는 것은 Consumer이다.
package com.devkuma.basic.completablefuture;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class SupplyAndExecuteAndConsume {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Supplier<Integer> initValueSupplier = () -> 100;
Function<Integer, Integer> multiply = value -> value * 2;
Consumer<Integer> valueConsumer = value -> System.out.println(value);
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(initValueSupplier)
.thenApplyAsync(multiply)
.thenAcceptAsync(valueConsumer);
future.get();
}
}
실행 결과:
200
- 기본적으로는 이전의 패턴과 같다.
CompletableFuture.thenApplyAsync(Function)CompletableFuture의 결과의 값을 건네주면서Function의 처리를 실행한다.
하나의 처리를 여러 스레드에서 수행하고, 첫 번째 결과를 사용하여 다른 처리를 수행한다.
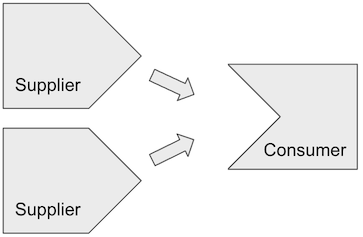
Supplier에서 처리한 결과를 반환하고, Consumer에서 받은 값을 사용하여 처리한다.
package com.devkuma.basic.completablefuture;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class RaceAndConsume {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Supplier<Integer> initValueSupplier = () -> 100;
Supplier<Integer> anotherValueSupplier = () -> 200;
Consumer<Integer> valueConsumer = value -> System.out.println(value);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(initValueSupplier);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(anotherValueSupplier);
future1.acceptEitherAsync(future2, valueConsumer).get();
}
}
실행 결과:
100 or 200
CompletableFuture.acceptEitherAsync(CompletableFuture, Consumer)- 먼저 결과가 나온 것을 사용하여
Consumer처리를 하게 된다.
- 먼저 결과가 나온 것을 사용하여
하나의 처리를 여러 스레드에서 수행하고, 첫 번째 결과를 사용하여 다른 처리를 수행하고, 그 결과를 사용하여 다른 처리를 수행한다.
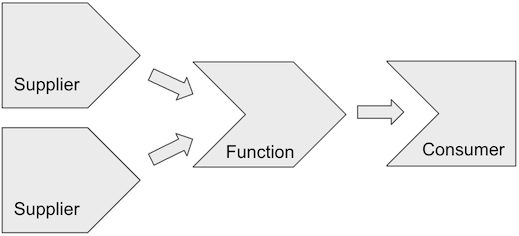
package com.devkuma.basic.completablefuture;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class RaceAndConsume2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Supplier<Integer> initValueSupplier = () -> 100;
Supplier<Integer> anotherValueSupplier = () -> 200;
Function<Integer, Integer> multiply = value -> value * 2;
Consumer<Integer> valueConsumer = value -> System.out.println(value);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(initValueSupplier);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(anotherValueSupplier);
future1.applyToEitherAsync(future2, multiply)
.thenAcceptAsync(valueConsumer)
.get();
}
}
실행 결과:
200 or 400